Faculty research

Topic 1: A study of the transfer system and credit banking system.
Research on the education transfer system and credit banking system: A basic education level was studied between February – March 2020.
The objectives were to 1) study the credit transfer system and the credit banking system, 2) study the factors that promote the credit banking system with the labor sector in the case study of province and the national level, and 3) present guidelines for promoting the credit banking system with the labor sector.
Descriptive research methods Population used in the research included representatives from educational institutions under the Office of the Basic Education Commission, educational institutions under local administrative organizations, private educational institutions, vocational institutions (administrators, teachers, students, parents), higher education institutions, (administrators, teachers, students and parents), representative of the Provincial Non-Formal Education Office, representatives of provincial industry, representatives of Provincial Chamber of Commerce, representatives of the establishments and representatives of provincial skill development of provinces in four regions obtained through specific selection according to criteria and recommendations of experts. The key informants included administrators, teachers, students, parents, and establishments.
Research team: Assistant Professor Dr. Fuangarun Preededilok, Dr. Doungkamol Bangchuad

Topic 2: Participation System in Organizing Area-based Education
The objectives of Participatory System in Area-Based Management in Education were to: 1) study and compare autonomous school models in different countries, 2) analyze lessons learned from case studies in Thailand that use autonomous school models in administration and management, and 3) propose development strategies of education management in the education system and enhance participation presents strategies Developing an education management system and creating participation
This research used a mixed method research design consisting of documentary research, interview, focus group and survey research. The results based on the objectives can be described as follows: 1. The models of autonomous school are different in each country; 2. Schools that use autonomous school models are under the same laws and regulations but in practice they are all still different and still face various obstacles; and 3. The development strategies of education management in the education system to enhance participation are comprised of six main strategies, 15secondary strategies, and 49 measures. Success factors are divided into 2 parts: external factors and internal factors. There are several cooperation models of area-based management in education such as the readiness model, network model, area-based model, partnership model and autonomous model.
Research team: Assistant Professor Dr. Fuangarun Preededilok, Dr. Doungkamol Bangchuad

Topic 3: Guidelines to Promote Global Citizenship: Experiences from International (Oversea Experience)
Research on Guidelines to Promote Global Citizenship: Experiences from International. Education is the gateway to equality in society and providing the necessary education and skills will empower individuals to help create a better modern world by addressing the issue of Education First to create a big ripple effect in the education industry with three main goals: Put Every Child in School, Improve the Quality of Learning, and Foster Global Citizenship. The concept of education comes first, all three of these issues have received attention and are integrated into the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), which will be implemented in 2016 – 2030 respectively. Especially the issue of Foster Global Citizenship, which is new and attractive, and still quite a bit of knowledge and examples of concrete actions in practice. The Office of the Secretariat of the Education Council has therefore carried out a research project on ways to promote Global Citizenship.
Research team: Assistant Professor Dr. Fuangarun Preededilok, Dr. Doungkamol Bangchuad

Topic 4 Promoting International Education as an Education Hub: Trends and Directions
Research team: Professor Dr. Chanita Rukspollmuang, ; Assistant Professor Dr. Walai Isarangkun Na Ayutthaya, Assistant Professor Dr. Fuangarun Preededilok,
Assistant Professor Dr. Pongsin Viseshsiri and Associate Professor Dr. Achanya Rattanaubon

Topic 5: Culturally Relevant Constructionist Design
The project qualitatively explores 55 Thai 4th grade students, a teacher, and 7 community members from a low-income public school in Bangkok, Thailand in order to develop a design framework for creating school-based maker experiences that are culturally relevant to lower income Thai students. Co-teaching and co‑designing a two-year design-based research project named, “Little Builders,” I worked with a local science teacher to engage the students in a constructionist learning experience that involved designing and building social innovations to solve problems in their community. I propose the Culturally Relevant Constructionist Design framework as a way to (1) create constructionist learning experiences that align with students’ values and goals, and (2) engage important people in the students’ lives, such as teachers and community members, in the process of making.
Research team: Dr. SAWAROS THANAPORNSANGSUTH

Topic 6 : Factors Influencing High Academic Achievement of Stateless Migrant Children in Tak Province, Thailand
The knowledge gained from this study will contribute to the field of migrant education and could encourage policymakers and educators to implement education programmes to both meet the needs and enable the success of migrant children. This multi-case study examined five factors—family, individual, school/teacher, peer group, and community/culture—that influenced the academic achievement of migrant children. The key participants were six migrant children in Grade 6 in two Royal Thai Government schools in Mae Sot, Tak Province, Thailand, three class teachers, and six caregivers. Data were collected through semi-structured interviews and observations. Creswell’s five steps of qualitative data analysis was used: organising and preparing data, reading through all data, coding the data, interrelating the themes, and interpreting the meaning of themes. The seven themes were as follows: (1) the value of education; (2) parents/guardians as important agents to support their children’s education; (3) individual characteristics contributing to good grades; (4) the impact of peer relationships; (5) healthy relationships with school and teachers; (6) the power of the community; and (7) gratitude as a motivation for a high level of education.
Research team: Dr. Peson Chobphon
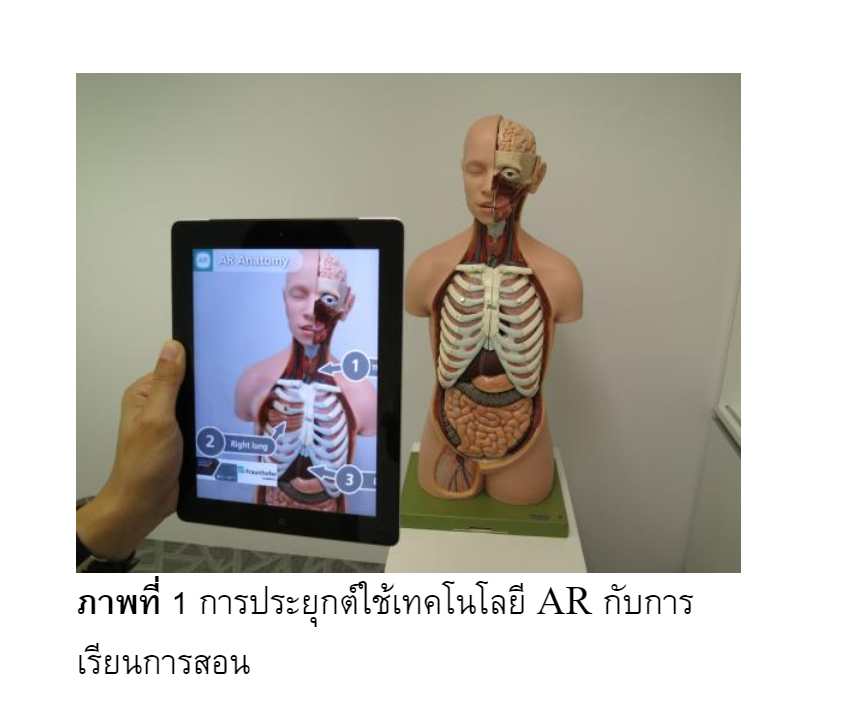

Topic 7: Nursing knowledge management with augmented reality technology and virtual classrooms
คณะผู้วิจัย : อาจารย์ ดร.เปศล ชอบผล, อาจารย์ ดร.งามนิตย์ รัตนานุกูล, อาจารย์ นฤมล พรหมภิบาล, อาจารย์ จิตรลดา สมประเสริฐ, อาจารย์ ดร.นิติบดี ศุขเจริญ

Topic 8: Learning Styles
Learning styles were divided into various categories according to students’ ideas. Systems of various learning styles which have been used for benefits to understand the learners were classified into 3 layers according to the characteristics of an onion. The outermost layer was the organization of learning styles observed in the form of preferences in learning methods arising from the learner’s interactions with the environment around them. The middle layer was a learning style depending on the information processing characteristics of the learners. The innermost layer was the learning model developed from the thoughts and personality of the learner. Measuring learning styles with the ability model indicated the style of each student. The findings revealed that that most used learning style was the concept of Kracha and Riceman, and, the most common learning styles were participatory and cooperative.
Research team: Dr. Peson Chobphon, Chiraphorn Phrakhunanan, Koraphin Ritthibut, Dr. Nitibodee Sukjaroen

Topic 9: THE KING’S PHILOSOPHY: LEARNING ANALYSIS OF NEW GENERATION FARMERS’ WAY OF LIFE
The objectives of this research were 1. to analyze new generation farmers’ way of life according to the King’s Philosophy and 2. to purpose new generation farmers’ way of life model according to the King’s Philosophy. The research cases were 26 new generation farmers by documentary research, content analysis, in-depth interview, non-participation observation. The research instruments were interview form and observation form. The results of research synthesis were: New generation farmers applied the King’s Philosophy which is the fighter in different context based on their own academic or skills expertise. The way of new generation agriculture life model was searching and developing themselves by “Philosophy of Life Identity” that started with self-understanding, then improved skills of apply theory to practice, and intended to work for the community. There were 3 elements of new generation farmers as 1. “Planning to have” as place, money, knowledge, friendship. 2. “Planning to be”: to decide their own life and 3. “Proper way of life” as balance, happiness and freedom. Moreover, both government and private agency supported the training based on new generation farmers’ need and followed up the performance to improve the training. In addition, universities and vocational education institutes also offered the agricultural entrepreneurship curriculum to form the new generation farmers as well.
This research aimed to analyze the work practices concepts and educational management for the continuation of local arts and cultures at the Border Patrol Police School and to present guidelines for teaching and learning management to continue local arts and cultures of the Border Patrol Police School according to the royal initiative of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn.
It was found that every Border Patrol Police school promoted the preservation of local cultures and traditions in different ways, such as creating a local curriculum, integrating it with other subjects, or organizing activities in the form of clubs under supervision of Border Patrol Police Division, government agencies, the private sector and communities.
There were different goals: for students to learn and participate in local cultural traditions, while others were for students to use their knowledge and skills to create income for themselves and their families. Guidelines for organizing education to preserve the local culture of the Border Patrol Police School had two approaches: both Top-down and Bottom-up. It started with listening to teachers’ needs by organizing a space to exchange knowledge and summarize knowledge to disseminate, systematically storing data, creating opportunities for the development of teachers’ educational knowledge in the form of an experimental space (Sandbox) and accumulating knowledge credits from work (Credit bank), providing knowledge and practice in integrating teaching and learning and writing local curriculum, setting up an alumni club and creating social media that collects products of the Border Patrol Police School for distribution.
Research team: Dr. Doungkamol Bangchuad

Topic 10: Factors Influencing Academic Achievement of Economically Disadvantaged Children in Remote Areas of Thailand: A Phenomenology Study
The purpose of this study was to investigate the factors influencing the academic success of economically disadvantaged children who resided in remote areas of Thailand. This study applied the phenomenology research methodology. The participants in this study were eight academically successful people who had already graduated at least at the bachelor degree level. They had been economically disadvantaged, residing in remote areas of Thailand and had obtained HRH Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn Scholarships. A semi-structured interview was applied as a means of collecting data. There were two rounds of one-on-one interviews with each participant and each round was at least one month apart. This study applied Creswell’s steps of data analysis; organising and preparing data, reading through all the data, coding the data, interrelating theme, and interpreting the meaning of theme. The five themes of factors influencing academic achievement that emerged were; aspirations and educational goals, personal characteristics of people who have academic achievement, significant others who inspired and supported, scholarships as opportunity creators, and schools and universities as agents for academic achievement.
Research team: Dr. Peson Chobphon.

Topic 11: Overseas Thai Dancing Education Instruction
Research on development of curriculum and guidelines for Thai dancing education instruction for students abroad.
The objectives were to study the problems, obstacles, and needs in Thai dancing education instruction for students abroad and to develop curriculum and guidelines for Thai dancing education instruction for students abroad. This research was initiated during the early stage of the COVID-19 pandemic situation. The teaching and learning management had to be greatly adjusted both to be able to develop Thai dancing skills and to transfer Thainess at the same time. Currently, most students were born and raised abroad; therefore, they had little interest in Thai culture. However, their parents still get aware of the importance and encourage them to study with the aim of assimilating the culture and having the opportunity to perform at various events under the operation of the committee in each temple. Those involved agreed that a curriculum, a guideline for Thai dancing education instruction and evaluation should be created to solve the problem of changing teachers and help students become enthusiastic about learning in order to get the higher level. Volunteer teachers should have a passion for teaching and be able to adapt in rapidly changing situations. The curriculum and the guidelines for education instruction were divided into 6 levels according to the abilities of the students. Each level will consist of content, teaching media and songs appropriate for learning at each level.
Research team: Saowaporn Bunchuay, Asst. Prof. Dr. Ubonwan Hongwittayakorn, Asst. Prof. Dr. Duangkamon Bangchuad, and Ajarn Prewfon Thiansri.

Topic 12: Arts and Cultures in Border Patrol Police School
Research on Guidelines for Organizing Education to Preserve Local Arts and Cultures according to the Royal Initiative of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn: A Case Study of the Border Patrol Police School
By Asst. Prof. Dr. Duangkamon Bangchuat, Asst. Prof. Dr. Ubonwan Hongwittayakorn, Asst. Prof. Dr. Panya Akkaraputthaphong, Asst. Prof. Dr. Peson Chobphon and Mr. Supachai Srinual
This research aimed to analyze the concepts, working principles, and education instruction to preserve local arts and culture of Border Patrol Police School and to present guidelines for education instruction to preserve the local arts and culture of Border Patrol Police School according to the royal initiative of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn. The findings revealed that every Border Patrol Police school promoted the preservation of local culture and traditions in different ways, such as creating a local curriculum, integrating the curriculum with other subjects or organizing activities in the form of clubs participating in the operations with Border Patrol Police Division, government agencies, private sectors, and communities. Different goals were set for students to learn and participate in local cultural traditions, while some others are for students to use their knowledge and skills to later gain income for themselves and their families. Guidelines for education instruction to preserve the local culture of the Border Patrol Police School had two approaches: both Top-down and Bottom-up. They started with listening to the needs of teachers by organizing a space to exchange and summarize knowledge to distribute systematic data collection, creating opportunities for the development of teachers’ educational knowledge in the form of an experimental space (Sandbox), accumulating knowledge credits from work (Credit Bank), providing knowledge and taking action on integrating education instruction and local curricula preparation, setting up an alumni club, and creating social media to collect and distribute products of the Border Patrol Police School.

Topic 13: History of Tha Pla, Uttaradit
Research on Sirikit Dam and Tha Pla District Uttaradit Province: Dimensions of local history for sustainable development
By Asst. Prof. Dr. Duangkamon Bangchuat, Asst. Prof. Dr. Ubonwan Hongwittayakorn, Assistant Professor Dr. Fuangarun Preededilok, and others.
The purposes of this research were to study the way of life in the local history of Tha Pla District, Uttaradit Province, to analyze factors, conditions, and benefits received from the joint development of the Nan River Basin and Sirikit Dam from the past to the present, and to present the relationship of the Tha Pla community with Sirikit Dam that affects sustainable development. It was qualitative research. The highlight of this research was the research methodology that was adapted to the COVID pandemic situation. Normally, the researchers collected data of local history research on their own, but in this research, the data was collected jointly with local history researchers and research assistants, the school teachers and research youth, the students in the area. In addition to the result of the study of lifestyles, it was a process of creating local researchers who have knowledge, understanding and awareness of the values of their own localities as well.